This post discusses how to configure Caddy and AdGuard Home as rootless Podman containers using podman compose and iptables.
Background
The beauty of rootless containers is that they are, well, rootless; they “elegantly constrain privileges by using a subuid/subgid map to enable the container to run in the user namespace but with what feels like full root privileges”1.
What if you want to solve a rootful problem with a rootless solution? What if you want to ignore “cases where running a container as root makes sense”2 and run containers as non-root anyways (perhaps to mitigate the risks of container escape)? That is precisely the question we are answering today!
Caddy (web server) and AdGuard Home (DNS server) bind to privileged ports, and must therefore either be run as root or the ports must be made unprivileged. The former is an obvious solution, and not what we are interested in here, while the latter is less so; common advice is to run sudo sysctl net.ipv4.ip_unprivileged_port_start = 53 on the host, however this makes all ports 53 unprivileged!
A better solution, which seemingly obtains the best of both worlds, is to (1) configure firewall rules to redirect traffic from the privileged ports to corresponding unprivileged ports and (2) bind our rootless containers to these unprivileged ports34.
Setup
1. System Configurations
In the last post, we installed ufw to make managing iptables rules a little simpler. We can use ufw / iptables to redirect traffic using network address translation (NAT) - in our case, we want to translate requests from privileged ports (e.g. 53, 80, 443) to unprivileged ports (e.g. 5300, 8000, 4443).
1.1. Update Firewall Rules
As we want to allow HTTP(S) and DNS connections (for Caddy and AdGuard Home, respectively), we need to open those ports:
sudo ufw allow http
sudo ufw allow https
sudo ufw allow 53The unprivileged ports must be opened up as well (as for why, you will see in a moment):
sudo ufw allow 4443
sudo ufw allow 5300
sudo ufw allow 8000
sudo ufw allow 8080
sudo ufw allow 8081
sudo ufw allow 80821.2. Configuring NAT Rules
Now we define the rules followed to perform the actual routing / translation. Using the privileged → unprivileged mapping defined earlier, we can add the following iptables rules to the end of /etc/ufw/before.rules:
*nat
:PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0]
:POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0]
-A PREROUTING -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 5300
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --dport 53 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 5300
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 8000
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 4443
-A PREROUTING -p udp -m udp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 4443
COMMIT
These rules instruct the firewall to redirect UDP or TCP DNS requests from 53 → 5300, TCP HTTP requests from 80 → 8000, and UDP or TCP HTTPS requests from 443 → 4443 as soon as they come in5. The reason why “the unprivileged ports [5300, 8000, and 4443] must be opened up as well” is that the PREROUTING chain of the nat table redirects incoming packets before a routing decision is made. Thus, ports 5300, 8000, and 4443 must be allow-listed, otherwise the routing decision will always be a bit fat DROP. For context, please consult the following diagram:
Note
Full credit for the following diagram goes to Phil Hagen! Find the original post here.
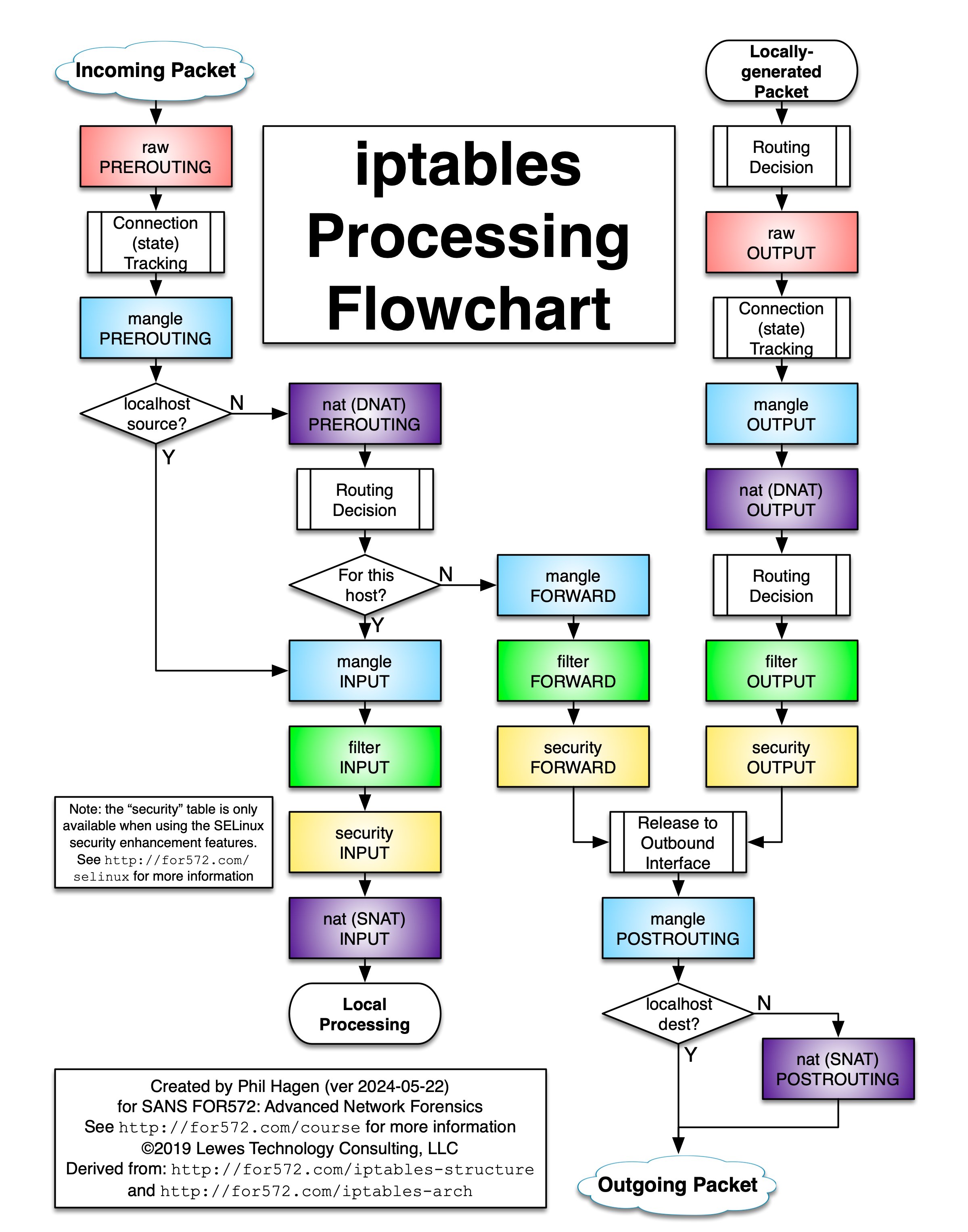
As far as I can tell (based on the man page5 and relevant guides6789), there does not exist an (obvious) better way to perform port redirection on incoming packets after the routing decision is made, hence this is the solution I am sticking with. I accept the risk of allow-listing select unprivileged ports (since they are already accessible via the privileged ports, after all).
1.3. Reload
For the preceding changes to come into effect, ufw must be reloaded like so:
sudo ufw reloadNow, all that’s left is to deploy the services listening on these unprivileged ports.
2. User Services
Note
All user services are defined in my homelab repository. Each service will contain at least:
.env: Environment variables to configure the servicecompose.yml: The compose file which defines each of the microservices which comprise the serviceREADME.md: Documentation for the service
2.1. AdGuard Home
AdGuard Home acts as my DNS server and is configured to perform DNS rewrites such that any request for a *.lab domain will be resolved to my server’s IP address. For example, requests for adguard.com will be fulfilled by an upstream DNS server, while requests for adguard.lab will be fulfilled by AdGuard Home itself and resolve to my server’s IP address.
Configuration
Deploying AdGuard Home is quite simple as it is only a single container requiring two volumes and three port bindings. It can be configured as follows.
Note
See https://github.com/AdguardTeam/AdGuardHome/wiki/Docker for full configuration details
.env
WORK_DIR=<...>
CONF_DIR=<...>
compose.yml
name: adguardhome
services:
server:
container_name: adguardhome_server
image: docker.io/adguard/adguardhome:v0.107.71
volumes:
- ${WORK_DIR}:/opt/adguardhome/work
- ${CONF_DIR}:/opt/adguardhome/conf
ports:
- '5300:53/udp' # unprivileged, firewall will redirect 53 -> 5300
- '5300:53/tcp' # unprivileged, firewall will redirect 53 -> 5300
- '8080:80/tcp'
restart: alwaysDeploy
podman compose up -d2.2. Caddy
Caddy acts as a reverse proxy and is configured to forward traffic from specific .lab domains (redirected here by AdGuard Home) to the corresponding service. For example, traffic bound for adguard.lab is forwarded back to the container running AdGuard Home.
Aside
Before proceeding to the configuration, I want to first clarify the second half of why “the unprivileged ports [8080, 8081, and 8082] must be opened up as well”. It all comes down to pasta - the networking application (Pack A Subtle Tap Abstraction), not the food. As of Podman 5.0, “pasta” is the default networking application10, which has the following implication:
Pasta, by default, does not use Network Address Translation (NAT). This means it will copy the host address into the container as well, which means both the host and container namespace use the same IP address. This, in turn, means if you try to connect to the host IP from the container, it will refer to itself, not the host.
To overcome this problem, an IP address is mapped to the host and the host.containers.internal is mapped to this IP address in /etc/hosts. Thus, host.containers.internal resolves to the host; however, it must be noted that requests made to the host from the container are treated as incoming packets and the ports to which those packets are addressed must therefore be allow-listed.
My Caddy configuration uses host.containers.internal:<port> to address the service running on the host exposed on port <port>. Currently, the only such ports are 8080, 8081, and 8082, and, per the prior discussion, these ports must be opened on the firewall.
Note
That may have been more than “a moment”, but I hope you get the point!
Configuration
Deploying Caddy is almost as simple as deploying AdGuard Home as it, too, is a single container requiring three port bindings; however it also requires a conf directory containing a Caddyfile as a bind mount.
Note
See https://hub.docker.com/_/caddy/#docker-compose-example for full configuration details
.env
DATA_DIR=<...>
CONF_DIR=<...>
conf/Caddyfile
adguard.lab {
reverse_proxy host.containers.internal:8080
tls internal
}
# See part 6!
seafile.lab {
reverse_proxy host.containers.internal:8081
tls internal
}
# See part 6!
immich.lab {
reverse_proxy host.containers.internal:8082
tls internal
}
compose.yml
name: caddy
services:
caddy:
container_name: caddy_server
image: docker.io/caddy:2.11
ports:
- '8000:80/tcp' # unprivileged, firewall will redirect 80 -> 8000
- '4443:443/udp' # unprivileged, firewall will redirect 443 -> 4443
- '4443:443/tcp' # unprivileged, firewall will redirect 443 -> 4443
volumes:
- ${PWD}/conf:/etc/caddy
- ${DATA_DIR}:/data
- ${CONF_DIR}:/config
restart: alwaysDeploy
podman compose up -dExample
Accessing https://adguard.lab (for example) should:
- Trigger a DNS request for
adguard.lab - Result in AdGuard Home rewriting the response such that
adguard.lab→<server-ip-address> - Redirect the request to
<server-ip-address>:443 - Result in Caddy proxying the request from port
443to port8080on the server (i.e. the port running AdGuard Home’s web interface)
Summary
In this post, I described how to bind rootless containers to privileged ports and configure both AdGuard Home and Caddy in such a fashion. Together, they can be used to define custom local domains with HTTPS.
Footnotes
-
https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/hpc-containers-scale-using-podman ↩
-
https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/basic-security-principles-containers ↩
-
https://linuxconfig.org/how-to-bind-a-rootless-container-to-a-privileged-port-on-linux ↩
-
https://docs.redhat.com/en/documentation/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/security_guide/sec-configuring_nat_using_nftables#sec-Configuring_a_redirect_using_nftables ↩
-
https://wiki.nftables.org/wiki-nftables/index.php/Performing_Network_Address_Translation_(NAT) ↩
-
https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-port-redirection-with-iptables/ ↩
-
https://blog.podman.io/2024/10/podman-5-3-changes-for-improved-networking-experience-with-pasta/ ↩